Java培训实战教程之lucene初探
更新时间:2015年12月29日13时26分 来源:传智播客Java培训学院 浏览次数:
全文检索场景
当你在使用百度、Google搜索信息时,当你在淘宝、京东搜索商品时你知道这些都是使用的什么技术可以很快搜索你想要的东东吗?正是全文检索技术。
全文检索概念
全文检索是将整本书、整篇文章中的任意内容信息查找出来的检索。它可以根据需要获得全文中有关章、节、段、句、词等信息,计算机程序通过扫描文章中的每一个词,对每一个词建立一个索引,指明该词在文章中出现的次数和位置,当用户查询时根据建立的索引查找,类似于通过字典的检索字表查字的过程。
经过几年的发展,全文检索从最初的字符串匹配程序已经演进到能对超大文本、语音、图像、活动影像等非结构化数据进行综合管理的大型软件。
什么是Lucene
Lucene是apache下的一个开放源代码的全文检索引擎工具包。提供了完整的搜索引擎和索引引擎。Lucene的目的是为软件开发人员提供一个简单易用的工具包,以方便的在目标系统中实现全文检索的功能。
案例描述
我们以一个案例来研究全文检索过程:实现一个资源管理器的搜索功能,通过关键字搜索文件,凡是文件名或文件内容包括关键字的文件都需要找出来。
开发环境
从Lucene官方网站(http://lucene.apache.org/)下载Lucene4.3.10,并解压。
Lucene4.3.10要求Jdk使用1.7以上,本教程使用1.7.0_72版本。
开发工具:eclipse indigo
Lucene包:
lucene-core-4.10.3.jar---Lucene核心包
lucene-analyzers-common-4.10.3.jar----Lucene分析包
lucene-queryparser-4.10.3.jar ---Lucene查询包
其它:
commons-io-2.4.jar ---用于读取磁盘文件内容
junit-4.9.jar---用于单元测试
Lucene全文检索过程
全文检索包括索引和搜索两个过程,先对要搜索的信息创建索引,再从索引中搜索信息。
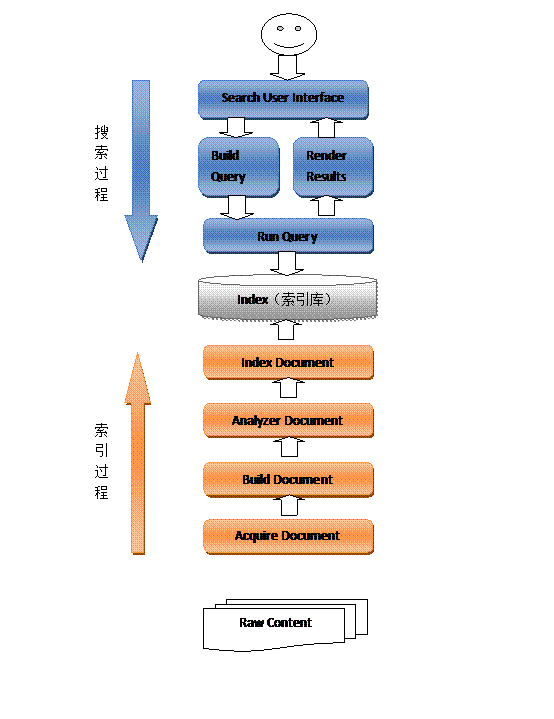
如下图:
1、黄色表示索引过程,对要搜索的原始内容进行索引构建一个索引库,索引过程包括:
确定原始内容即要搜索的内容--》采集文档--》创建文档--》分析文档--》索引文档
2、蓝色表示搜索过程,从索引库中搜索内容,搜索过程包括:
用户通过搜索界面--》创建查询--》执行搜索,从索引库搜索--》渲染搜索结果
第一步:确定原始内容
原始内容是指要索引和搜索的内容。原始内容包括互联网上的网页、数据库中的数据、磁盘上的文件等。
本案例中的原始内容就是磁盘上的文件(本教程只搜索.txt文件),如下图: 第二步:获取原始内容
第二步:获取原始内容
从互联网上、数据库、文件系统中等获取需要搜索的原始信息,这个过程就是信息采集,信息采集的目的是为了对原始内容进行索引。
Lucene本身不提供信息采集的功能,这里我们通过Java流程读取磁盘文件的内容。
第三步:创建文档
获取原始内容的目的是为了索引,在索引前需要将原始内容创建成文档(Document),文档中包括一个一个的域(Field),域中存储内容。
这里我们可以将磁盘上的一个文件当成一个document,Document中包括一些Field(file_name文件名称、file_path文件路径、file_size文件大小、file_content文件内容),如下图:

注意:每个Document可以有多个Field,不同的Document可以有不同的Field,同一个Document可以有相同的Field(域名和域值都相同)
下边代码实现了从磁盘读取文件并创建文档的过程:
// 从文件创建Document
public static List<Document> file2Document(String folderPath)
throws IOException {
List<Document> list = new ArrayList<Document>();
File folder = new File(folderPath);
if (!folder.isDirectory()) {
return null;
}
// 获取目录 中的所有文件
File[] files = folder.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
//文件名称
String fileName = file.getName();
System.out.println(fileName);
if (fileName.lastIndexOf(".txt") > 0) {
// 文件内容
String fileContent = FileUtils.readFileToString(file);
//文件路径
String filePath = file.getAbsolutePath();
//文件大小
long fileSize = FileUtils.sizeOf(file);
//创建文档
Document doc = new Document();
//创建各各Field域
//文件名
Field field_fileName = new StringField("fileName", fileName, Store.YES);
//文件内容
Field field_fileContent = new TextField("fileContent", fileContent, Store.NO);
//文件大小
Field field_fileSize = new LongField("fileSize", fileSize, Store.YES);
//文件路径
Field field_filePath = new StoredField("filePath", filePath, Store.YES);
//将各各Field添加到文档中
doc.add(field_fileName);
doc.add(field_fileContent);
doc.add(field_fileSize);
doc.add(field_filePath);
list.add(doc);
}
}
return list;
}
第四步:分析文档
将原始内容创建为包含域(Field)的文档(document),需要再对域中的内容进行分析,分析的过程是经过对原始文档提取单词、将字母转为小写、去除标点符号、去除常用词等过程生成最终的语汇单元,可以将语汇单元理解为一个一个的单词。
比如下边的文档经过分析如下:
原文档内容:
Lucene is a Java full-text search engine. Lucene is not a complete
application, but rather a code library and API that can easily be used
to add search capabilities to applications.
分析后得到的语汇单元:
lucene、java、full、search、engine。。。。
第五步:创建索引
对所有文档分析得出的语汇单元进行索引,索引的目的是为了搜索,最终要实现只搜索被索引的语汇单元从而找到Document(文档)。
注意:创建索引是对语汇单元索引,通过词语找文档,这种索引的结构叫倒排索引结构。
传统方法是根据文件找到该文件的内容,在文件内容中匹配搜索关键字,这种方法是顺序扫描方法,数据量大、搜索慢。
倒排索引结构是根据内容(词语)找文档,如下图: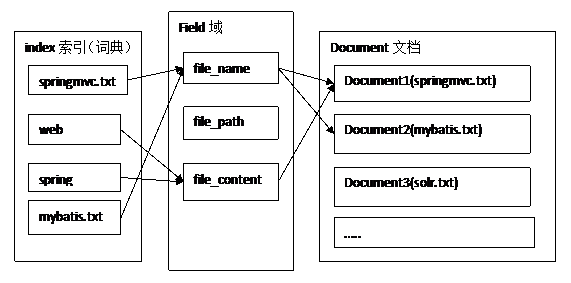
根据左边的索引词典可以找到词对应的文档。“springmvc.txt”这个词在Document1(springmvc.txt) ,“web”和“spring”在Document1、Document2中都存在,词是通过Field和Document文档联系起来的。
倒排索引结构也叫反向索引结构,包括索引和文档两部分,索引即词汇表,它的规模较小,而文档集合较大。
使用分析器分析并创建索引过程代码如下:
public class IndexTest {
// 索引源,即源数据目录
private static String searchSource = "F:\\develop\\lucene\\searchsource";
// 索引目标地址
private static String indexFolder = "F:\\develop\\lucene\\indexdata";
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() {
try {
//从目录中读取文件内容并创建Document文档
List<Document> docs = IndexUtils.file2Document(searchSource);
//创建分析器,standardAnalyzer标准分析器
Analyzer standardAnalyzer = new IKAnalyzer();
// 指定索引存储目录
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexFolder));
//创建索引操作配置对象
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_4_10_3,
standardAnalyzer);
// 定义索引操作对象indexWriter
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,indexWriterConfig);
// 遍历目录 下的文件生成的文档,调用indexWriter方法创建索引
for (Document document : docs) {
indexWriter.addDocument(document);
}
// 索引操作流关闭
indexWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
第六步:搜索文件
根据文件名称搜索文件,需要经过以下步骤:
1)指定索引目录地址,搜索就是从索引中搜索匹配的词语
// 指定索引目录地址,
private static String indexFolder = "F:\\develop\\lucene\\indexdata";
2)创建Query构建查询语法 (可以理解为和关系数据库的Sql作用一样)
// 创建查询对象,根据文件名称域搜索匹配文件名称的文档
Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("fileName", "springmvc_test.txt"));
3)创建IndexReader读取索引文件
// 指定索引目录
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexFolder));
// 定义IndexReader
IndexReader reader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
4)创建IndexSearcher执行搜索
// 创建indexSearcher
IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(reader);
// 执行搜索
TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 100);
5)通过TopDocs获取搜索结果
// 提取搜索结果
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs;
6)遍历结果,从Document中获取Field内容
for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : scoreDocs) {
// 文档id
int docID = scoreDoc.doc;
// 得到文档
Document doc = indexSearcher.doc(docID);
// 输出 文件内容
System.out.println("------------------------------");
System.out.println("文件名称 =" + doc.get("fileName"));
System.out.println("文件大小 =" + doc.get("fileSize"));
System.out.println("文件内容 =" + doc.get("fileContent"));
}
完整代码如下:
public class SearchTest {
// 指定索引目录地址,
private static String indexFolder = "F:\\develop\\lucene\\indexdata";
//查询方法
@Test
public void testTermQuery() throws IOException {
// 创建查询对象,根据文件名称域搜索匹配文件名称的文档
Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("fileName", "springmvc_test.txt"));
// 指定索引目录
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexFolder));
// 定义IndexReader
IndexReader reader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
// 创建indexSearcher
IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(reader);
// 执行搜索
TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 100);
// 提取搜索结果
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs;
System.out.println("共搜索到总记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits);
for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : scoreDocs) {
// 文档id
int docID = scoreDoc.doc;
// 得到文档
Document doc = indexSearcher.doc(docID);
// 输出 文件内容
System.out.println("------------------------------");
System.out.println("文件名称 =" + doc.get("fileName"));
System.out.println("文件大小 =" + doc.get("fileSize"));
System.out.println("文件内容 =" + doc.get("fileContent"));
}
}
当你在使用百度、Google搜索信息时,当你在淘宝、京东搜索商品时你知道这些都是使用的什么技术可以很快搜索你想要的东东吗?正是全文检索技术。
全文检索概念
全文检索是将整本书、整篇文章中的任意内容信息查找出来的检索。它可以根据需要获得全文中有关章、节、段、句、词等信息,计算机程序通过扫描文章中的每一个词,对每一个词建立一个索引,指明该词在文章中出现的次数和位置,当用户查询时根据建立的索引查找,类似于通过字典的检索字表查字的过程。
经过几年的发展,全文检索从最初的字符串匹配程序已经演进到能对超大文本、语音、图像、活动影像等非结构化数据进行综合管理的大型软件。
什么是Lucene
Lucene是apache下的一个开放源代码的全文检索引擎工具包。提供了完整的搜索引擎和索引引擎。Lucene的目的是为软件开发人员提供一个简单易用的工具包,以方便的在目标系统中实现全文检索的功能。
案例描述
我们以一个案例来研究全文检索过程:实现一个资源管理器的搜索功能,通过关键字搜索文件,凡是文件名或文件内容包括关键字的文件都需要找出来。
开发环境
从Lucene官方网站(http://lucene.apache.org/)下载Lucene4.3.10,并解压。
Lucene4.3.10要求Jdk使用1.7以上,本教程使用1.7.0_72版本。
开发工具:eclipse indigo
Lucene包:
lucene-core-4.10.3.jar---Lucene核心包
lucene-analyzers-common-4.10.3.jar----Lucene分析包
lucene-queryparser-4.10.3.jar ---Lucene查询包
其它:
commons-io-2.4.jar ---用于读取磁盘文件内容
junit-4.9.jar---用于单元测试
Lucene全文检索过程
全文检索包括索引和搜索两个过程,先对要搜索的信息创建索引,再从索引中搜索信息。
如下图:
1、黄色表示索引过程,对要搜索的原始内容进行索引构建一个索引库,索引过程包括:
确定原始内容即要搜索的内容--》采集文档--》创建文档--》分析文档--》索引文档
2、蓝色表示搜索过程,从索引库中搜索内容,搜索过程包括:
用户通过搜索界面--》创建查询--》执行搜索,从索引库搜索--》渲染搜索结果

第一步:确定原始内容
原始内容是指要索引和搜索的内容。原始内容包括互联网上的网页、数据库中的数据、磁盘上的文件等。
本案例中的原始内容就是磁盘上的文件(本教程只搜索.txt文件),如下图:

从互联网上、数据库、文件系统中等获取需要搜索的原始信息,这个过程就是信息采集,信息采集的目的是为了对原始内容进行索引。
Lucene本身不提供信息采集的功能,这里我们通过Java流程读取磁盘文件的内容。
第三步:创建文档
获取原始内容的目的是为了索引,在索引前需要将原始内容创建成文档(Document),文档中包括一个一个的域(Field),域中存储内容。
这里我们可以将磁盘上的一个文件当成一个document,Document中包括一些Field(file_name文件名称、file_path文件路径、file_size文件大小、file_content文件内容),如下图:

注意:每个Document可以有多个Field,不同的Document可以有不同的Field,同一个Document可以有相同的Field(域名和域值都相同)
下边代码实现了从磁盘读取文件并创建文档的过程:
// 从文件创建Document
public static List<Document> file2Document(String folderPath)
throws IOException {
List<Document> list = new ArrayList<Document>();
File folder = new File(folderPath);
if (!folder.isDirectory()) {
return null;
}
// 获取目录 中的所有文件
File[] files = folder.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
//文件名称
String fileName = file.getName();
System.out.println(fileName);
if (fileName.lastIndexOf(".txt") > 0) {
// 文件内容
String fileContent = FileUtils.readFileToString(file);
//文件路径
String filePath = file.getAbsolutePath();
//文件大小
long fileSize = FileUtils.sizeOf(file);
//创建文档
Document doc = new Document();
//创建各各Field域
//文件名
Field field_fileName = new StringField("fileName", fileName, Store.YES);
//文件内容
Field field_fileContent = new TextField("fileContent", fileContent, Store.NO);
//文件大小
Field field_fileSize = new LongField("fileSize", fileSize, Store.YES);
//文件路径
Field field_filePath = new StoredField("filePath", filePath, Store.YES);
//将各各Field添加到文档中
doc.add(field_fileName);
doc.add(field_fileContent);
doc.add(field_fileSize);
doc.add(field_filePath);
list.add(doc);
}
}
return list;
}
第四步:分析文档
将原始内容创建为包含域(Field)的文档(document),需要再对域中的内容进行分析,分析的过程是经过对原始文档提取单词、将字母转为小写、去除标点符号、去除常用词等过程生成最终的语汇单元,可以将语汇单元理解为一个一个的单词。
比如下边的文档经过分析如下:
原文档内容:
Lucene is a Java full-text search engine. Lucene is not a complete
application, but rather a code library and API that can easily be used
to add search capabilities to applications.
分析后得到的语汇单元:
lucene、java、full、search、engine。。。。
第五步:创建索引
对所有文档分析得出的语汇单元进行索引,索引的目的是为了搜索,最终要实现只搜索被索引的语汇单元从而找到Document(文档)。
注意:创建索引是对语汇单元索引,通过词语找文档,这种索引的结构叫倒排索引结构。
传统方法是根据文件找到该文件的内容,在文件内容中匹配搜索关键字,这种方法是顺序扫描方法,数据量大、搜索慢。
倒排索引结构是根据内容(词语)找文档,如下图:

根据左边的索引词典可以找到词对应的文档。“springmvc.txt”这个词在Document1(springmvc.txt) ,“web”和“spring”在Document1、Document2中都存在,词是通过Field和Document文档联系起来的。
倒排索引结构也叫反向索引结构,包括索引和文档两部分,索引即词汇表,它的规模较小,而文档集合较大。
使用分析器分析并创建索引过程代码如下:
public class IndexTest {
// 索引源,即源数据目录
private static String searchSource = "F:\\develop\\lucene\\searchsource";
// 索引目标地址
private static String indexFolder = "F:\\develop\\lucene\\indexdata";
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() {
try {
//从目录中读取文件内容并创建Document文档
List<Document> docs = IndexUtils.file2Document(searchSource);
//创建分析器,standardAnalyzer标准分析器
Analyzer standardAnalyzer = new IKAnalyzer();
// 指定索引存储目录
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexFolder));
//创建索引操作配置对象
IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_4_10_3,
standardAnalyzer);
// 定义索引操作对象indexWriter
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,indexWriterConfig);
// 遍历目录 下的文件生成的文档,调用indexWriter方法创建索引
for (Document document : docs) {
indexWriter.addDocument(document);
}
// 索引操作流关闭
indexWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
第六步:搜索文件
根据文件名称搜索文件,需要经过以下步骤:
1)指定索引目录地址,搜索就是从索引中搜索匹配的词语
// 指定索引目录地址,
private static String indexFolder = "F:\\develop\\lucene\\indexdata";
2)创建Query构建查询语法 (可以理解为和关系数据库的Sql作用一样)
// 创建查询对象,根据文件名称域搜索匹配文件名称的文档
Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("fileName", "springmvc_test.txt"));
3)创建IndexReader读取索引文件
// 指定索引目录
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexFolder));
// 定义IndexReader
IndexReader reader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
4)创建IndexSearcher执行搜索
// 创建indexSearcher
IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(reader);
// 执行搜索
TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 100);
5)通过TopDocs获取搜索结果
// 提取搜索结果
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs;
6)遍历结果,从Document中获取Field内容
for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : scoreDocs) {
// 文档id
int docID = scoreDoc.doc;
// 得到文档
Document doc = indexSearcher.doc(docID);
// 输出 文件内容
System.out.println("------------------------------");
System.out.println("文件名称 =" + doc.get("fileName"));
System.out.println("文件大小 =" + doc.get("fileSize"));
System.out.println("文件内容 =" + doc.get("fileContent"));
}
完整代码如下:
public class SearchTest {
// 指定索引目录地址,
private static String indexFolder = "F:\\develop\\lucene\\indexdata";
//查询方法
@Test
public void testTermQuery() throws IOException {
// 创建查询对象,根据文件名称域搜索匹配文件名称的文档
Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("fileName", "springmvc_test.txt"));
// 指定索引目录
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexFolder));
// 定义IndexReader
IndexReader reader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
// 创建indexSearcher
IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(reader);
// 执行搜索
TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 100);
// 提取搜索结果
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs;
System.out.println("共搜索到总记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits);
for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : scoreDocs) {
// 文档id
int docID = scoreDoc.doc;
// 得到文档
Document doc = indexSearcher.doc(docID);
// 输出 文件内容
System.out.println("------------------------------");
System.out.println("文件名称 =" + doc.get("fileName"));
System.out.println("文件大小 =" + doc.get("fileSize"));
System.out.println("文件内容 =" + doc.get("fileContent"));
}
}


















 AI智能应用开发
AI智能应用开发 AI大模型开发(Python)
AI大模型开发(Python) AI鸿蒙开发
AI鸿蒙开发 AI嵌入式+机器人开发
AI嵌入式+机器人开发 AI运维
AI运维 AI测试
AI测试 跨境电商运营
跨境电商运营 AI设计
AI设计 AI视频创作与直播运营
AI视频创作与直播运营 微短剧拍摄剪辑
微短剧拍摄剪辑 C/C++
C/C++ 狂野架构师
狂野架构师


 http://www.itcast.cn/javaee
http://www.itcast.cn/javaee 


















